The classic one-line definition of Knowledge Management was offered up by Tom Davenport early on (Davenport, 1994): “Knowledge Management is the process of capturing, distributing, and effectively using knowledge.” Probably no better or more succinct single-line definition has appeared since.
However, Knowledge Management can best and most quickly be explained by recapping its origins. Later in this article, its stages of development will also be recapped.
The Origins of KM
The concept and the terminology of KM sprouted within the management consulting community. When the Internet arose, those organizations quickly realized that an intranet, an in-house subset of the Internet, was a wonderful tool with which to make information accessible and to share it among the geographically dispersed units of their organizations. Not surprisingly, they quickly realized that in building tools and techniques such as dashboards, expertise locators, and best practice (lessons learned) databases, they had acquired an expertise which was in effect a new product that they could market to other organizations, particularly to organizations which were large, complex, and dispersed. However, a new product needs a name, and the name that emerged was Knowledge Management. The term apparently was first used in its current context at McKinsey in 1987 for an internal study on their information handling and utilization (McInerney and Koenig, 2011). KM went public, as it were, at a conference in Boston in 1993 organized by Ernst and Young (Prusak 1999). Note that Davenport was at E&Y when he wrote the definition above.
Those consulting organizations quickly disseminated the principles and the techniques of KM to other organizations, to professional associations, and to disciplines. The timing was propitious, as the enthusiasm for intellectual capital (see below) in the 1980s, had primed the pump for the recognition of information and knowledge as essential assets for any organization.
What is KM trying to accomplish?
Rich, Deep, and Open Communication
First, KM can very fruitfully be seen as the undertaking to replicate, indeed to create, the information environment known to be conducive to successful R&D—rich, deep, and open communication and information access—and to deploy it broadly across the firm. It is almost trite now to observe that we are in the post-industrial information age and that we are all information workers. Furthermore, the researcher is, after all, the quintessential information worker. Peter Drucker once commented that the product of the pharmaceutical industry wasn’t pills, it was information. The research domain, and in particular the pharmaceutical industry, has been studied in depth with a focus on identifying the organizational and cultural environmental aspects that lead to successful research (Koenig, 1990, 1992). The salient aspect that emerges with overwhelming importance is that of rich, deep, and open communications, not only within the firm, but also with the outside world. The logical conclusion, then, is to attempt to apply those same successful environmental aspects to knowledge workers at large, and that is precisely what KM attempts to do.
Situational Awareness
Second, Situational Awareness is a term only recently, beginning in 2015, used in the context of KM. The term, however, long precedes KM. It first gained some prominence in the cold war era when studies were commissioned by all of the major potential belligerents to try to identify what characteristics made a good fighter pilot. The costs of training a fighter pilot were huge, and if the appropriate characteristics leading to success could be identified, that training could be directed to the most appropriate candidates, and of those trained the most appropriate could be selected for front-line assignment. However, the only solid conclusion of those studies was that the salient characteristic of a good fighter pilot was excellent “situational awareness.” The problem was that no good predictive test for situational awareness could be developed.
The phrase then retreated into relative obscurity until it was resuscitated by Jeff Cooper, a firearms guru, and others in the context of self-defense. How do you defend and protect yourself? The first step is to be alert and to establish good situational awareness. From there the phrase entered the KM vocabulary. The role of KM is to create the capability for the organization to establish excellent situational awareness and consequently to make the right decisions.
A new definition of KM
A few years after the Davenport definition, the Gartner Group created another definition of KM, which has become the most frequently cited one (Duhon, 1998), and it is given below:
"Knowledge management is a discipline that promotes an integrated approach to identifying, capturing, evaluating, retrieving, and sharing all of an enterprise's information assets. These assets may include databases, documents, policies, procedures, and previously un-captured expertise and experience in individual workers."
The one real lacuna of this definition is that it, too, is specifically limited to an organization’s own information and knowledge assets. KM as conceived now, and this expansion arrived early on, includes relevant information assets from wherever relevant. Note, however, the breadth implied for KM by calling it a “discipline.”
Both definitions share a very organizational and corporate orientation. KM, historically at least, was primarily about managing the knowledge of and in organizations. Rather quickly, however, the concept of KM became much broader than that.
A graphic map of Knowledge Management
What is still probably the best graphic to try to set forth what constitutes KM, is the graphic developed by IBM for the use of their own KM consultants. It is based upon the distinction between collecting stuff (content) and connecting people. The presentation here includes some minor modifications, but the captivating C, E, and H mnemonics are entirely IBM's:
| Graphic Map of KM |
COLLECTING (STUFF) &
CODIFICATION |
CONNECTING (PEOPLE) &
PERSONALIZATION |
DIRECTED
INFORMATION & KNOWLEDGE SEARCH
EXPLOIT
|
(HARVEST)
|
(HARNESS)
|
SERENDIPITY &
BROWSING
EXPLORE
|
(HUNTING)
|
(HYPOTHESIZE)
|
From: Tom Short, Senior consultant, Knowledge Management, IBM Global Services
(Note however the comments below under “Tacit.”) | ||
OK, what does KM actually consist of?
In short, what are the operational components of a KM system? This is, in a way, the most straightforward way of explaining what KM is—to delineate what the operational components are that constitute what people have in mind when they talk about a KM system.
(1) Content Management
So what is involved in KM? The most obvious is the making of the organization's data and information available to the members of the organization through dashboards, portals, and with the use of content management systems. Content Management, sometimes known as Enterprise Content Management, is the most immediate and obvious part of KM. For a wonderful graphic snapshot of the content management domain go to realstorygroup.com and look at their Content Technology Vendor Map. This aspect of KM might be described as Librarianship 101, putting your organization’s information and data up online, plus selected external information, and providing the capability to seamlessly shift to searching, more or less, the entire web. The term most often used for this is Enterprise Search. This is now not just a stream within the annual KMWorld Conference, but has become an overlapping conference in its own right. See the comments below under the “Third Stage of KM” section.
(2) Expertise Location
Since knowledge resides in people, often the best way to acquire the expertise that you need is to talk with an expert. Locating the right expert with the knowledge that you need, though, can be a problem, particularly if, for example, the expert is in another country. The basic function of an expertise locator system is straightforward: it is to identify and locate those persons within an organization who have expertise in a particular area. These systems are now commonly known as expertise location systems. In the early days of KM the term ‘Yellow Pages” was commonly used, but now that term is fast disappearing from our common vocabulary, and expertise location is, in any case, rather more precise.
There are typically three sources from which to supply data for an expertise locator system: (1) employee resumes, (2) employee self-identification of areas of expertise (typically by being requested to fill out a form online), and (3) algorithmic analysis of electronic communications from and to the employee. The latter approach is typically based on email traffic but can include other social networking communications such as Twitter, Facebook, and Linkedin. Several commercial software packages to match queries with expertise are available. Most of them have load-balancing schemes so as not to overload any particular expert. Typically such systems rank the degree of presumed expertise and will shift a query down the expertise ranking when the higher choices appear to be overloaded. Such systems also often have a feature by which the requester can flag the request as a priority, and the system can then match high priority to high expertise rank.
(3) Lessons Learned
Lessons Learned databases are databases that attempt to capture and make accessible knowledge, typically “how to do it” knowledge, that has been operationally obtained and normally would not have been explicitly captured. In the KM context, the emphasis is upon capturing knowledge embedded in personal expertise and making it explicit. The lessons learned concept or practice is one that might be described as having been birthed by KM, as there is very little in the way of a direct antecedent. Early in the KM movement, the phrase most often used was "best practices," but that phrase was soon replaced with "lessons learned." The reasons were that "lessons learned" was a broader and more inclusive term and because "best practice" seemed too restrictive and could be interpreted as meaning there was only one best practice in a situation. What might be a best practice in North American culture, for example, might well not be a best practice in another culture. The major international consulting firms were very aware of this and led the movement to substitute the new more appropriate term. "Lessons Learned" became the most common hallmark phrase of early KM development.
The idea of capturing expertise, particularly hard-won expertise, is not a new idea. One antecedent to KM that we have all seen portrayed was the World War II debriefing of pilots after a mission. Gathering military intelligence was the primary purpose, but a clear and recognized secondary purpose was to identify lessons learned, though they were not so named, to pass on to other pilots and instructors. Similarly, the U. S. Navy Submarine Service, after a very embarrassing and lengthy experience of torpedoes that failed to detonate on target, and an even more embarrassing failure to follow up on consistent reports by submarine captains of torpedo detonation failure, instituted a mandatory system of widely disseminated "Captain's Patrol Reports." The intent, of course, was to avoid any such fiasco in the future. The Captain's Patrol Reports, however, were very clearly designed to encourage analytical reporting, with reasoned analyses of the reasons for operational failure and success. It was emphasized that a key purpose of the report was both to make recommendations about strategy for senior officers to mull over, and recommendations about tactics for other skippers and submariners to take advantage of (McInerney and Koenig, 2011).
The military has become an avid proponent of the lessons learned concept. The phrase the military uses is "After Action Reports." The concept is very simple: make sure that what has been learned from experience is passed on, and don't rely on the participant to make a report. There will almost always be too many things immediately demanding that person's attention after an action. There must be a system whereby someone, typically someone in KM, is assigned the responsibility to do the debriefing, to separate the wheat from the chaff, to create the report, and then to ensure that the lessons learned are captured and disseminated. The experiences in Iraq, Afghanistan, and Syria have made this process almost automatic in the military.
The concept is by no means limited to the military. Larry Prusak (2004) maintains that in the corporate world the most common cause of KM implementation failure is that so often the project team is disbanded and the team members almost immediately reassigned elsewhere before there is any debriefing or after-action report assembled. Any organization where work is often centered on projects or teams needs to pay very close attention to this issue and set up an after-action mechanism with clearly delineated responsibility for its implementation.
A particularly instructive example of a "lesson learned" is one recounted by Mark Mazzie (2003), a well known KM consultant. The story comes from his experience in the KM department at Wyeth Pharmaceuticals. Wyeth had recently introduced a new pharmaceutical agent intended primarily for pediatric use. Wyeth expected it to be a notable success because, unlike its morning, noon, and night competitors, it needed to be administered only once a day, and that would make it much easier for the caregiver to ensure that the child followed the drug regimen, and it would be less onerous for the child. Sales of the drug commenced well but soon flagged. One sales rep (what the pharmaceutical industry used to call detail men), however, by chatting with her customers, discovered the reason for the disappointing sales and also recognized the solution. The problem was that kids objected strenuously to the taste of the drug, and caregivers were reporting to prescribing physicians that they couldn't get their kid to continue taking the drug, so the old stand-by would be substituted. The simple solution was orange juice, a swig of which quite effectively masked the offensive taste. If the sales rep were to explain to the physician that the therapy should be conveyed to the caregiver as the pill and a glass of orange juice taken simultaneously at breakfast, then there was no dissatisfaction and sales were fine.
The obvious question that arises is what is there to encourage the sales rep to share this knowledge? The sales rep is compensated based on salary (small), and bonus (large). If she shares the knowledge, she jeopardizes the size of her bonus, which is based on her comparative performance.
This raises the issue, discussed below, that KM is much more than content management. It extends to how does one structures the organizational culture to facilitate and encourage knowledge sharing, and that extends to how one structures the organization’s compensation scheme.
The implementation of a lessons learned system is complex both politically and operationally. Many of the questions surrounding such a system are difficult to answer. Are employees free to submit to the system un-vetted? Who, if anyone, is to decide what constitutes a worthwhile lesson learned? Most successful lessons learned implementations have concluded that such a system needs to be monitored and that there needs to be a vetting and approval mechanism for items that are posted as lessons learned.
How long do items stay in the system? Who decides when an item is no longer salient and timely? Most successful lessons learned systems have an active weeding or stratification process. Without a clearly designed process for weeding, the proportion of new and crisp items inevitably declines, the system begins to look stale, and usage and utility falls. Deletion, of course, is not necessarily loss and destruction. Using carefully designed stratification principles, items removed from the foreground can be archived and moved to the background but still made available. However, this procedure needs to be in place before things start to look stale, and a good taxonomically based retrieval system needs to be created.
These questions need to be carefully thought out and resolved, and the mechanisms designed and put in place, before a lessons-learned system is launched. Inattention can easily lead to failure and the creation of a bad reputation that will tar subsequent efforts.
(4) Communities of Practice (CoPs)
CoPs are groups of individuals with shared interests that come together in person or virtually to tell stories, to share and discuss problems and opportunities, discuss best practices, and talk over lessons learned (Wenger, 1998; Wenger & Snyder, 1999). Communities of practice emphasize, build upon, and take advantage of the social nature of learning within or across organizations. In small organizations, conversations around the water cooler are often taken for granted, but in larger, geographically distributed organizations, the water cooler needs to become virtual. Similarly, organizations find that when workers relinquish a dedicated company office to work online from home or on the road, the natural knowledge sharing that occurs in social spaces needs to be replicated virtually. In the context of KM, CoPs are generally understood to mean electronically linked communities. Electronic linkage is not essential, of course, but since KM arose in the consulting community from the awareness of the potential of intranets to link geographically dispersed organizations, this orientation is understandable.
A classic example of the deployment of CoPs comes from the World Bank. When James Wolfensohn became president in 1995, he focused on the World Bank's role in disseminating knowledge about development; he was known to say that the principal product of the World Bank was not loans, but rather the creation of knowledge about how to accomplish development. Consequently, he encouraged the development of CoPs and made that a focus of his attention. One World Bank CoP, for example, was about road construction and maintenance in arid countries and conditions. That CoP was encouraged to include and seek out not only participants and employees from the World Bank and its sponsored projects and from the country where the relevant project was being implemented, but also experts from elsewhere who had expertise in building roads in arid conditions, such as, for example, staff from the Australian Road Research Board and the Arizona Department of Highways. This is also a good example of the point that despite the fact that KM developed first in a very for-profit corporate context, it is applicable far more broadly, such as in the context of government and civil society.
The organization and maintenance of CoPs is not a simple or an easy task to undertake. As Durham (2004) points out, there are several key roles to be filled. She describes the key roles as manager, moderator, and thought leader. They need not necessarily be three separate people, but in some cases they will need to be. Some questions that need to be thought about and resolved are:
- Who fills the various roles of: manager, moderator, and thought leader?
- How is the CoP managed, and who will fill the management role?
- Who will have overall responsibility for coordinating and overseeing the various CoPs?
- Who looks for new members or suggests that the CoP may have outlived its usefulness?
- Who reviews the CoP for activity?
- Are postings open or does someone vet or edit the postings?
- How is the CoP kept fresh and vital?
- When and how (under what rules) are items removed?
- How are those items archived?
- How are the CoP files made retrievable? How do CoP leaders coordinate with the enterprise search/taxonomy function?
Another way to view KM is to look at the stages of KM’s Development
First Stage of KM: Information Technology
KM was initially driven primarily by IT, information technology, and the desire to put that new technology, the Internet, to work and see what it was capable of. That first stage has been described using a horse breeding metaphor as “by the internet out of intellectual capital,” the sire and the dam. The concept of intellectual capital, the notion that not just physical resources, capital, and manpower, but also intellectual capital (knowledge) fueled growth and development, provided the justification, the framework, and the seed. The availability of the internet provided the tool. As described above, the management consulting community jumped at the new capabilities provided by the Internet, using it first for themselves, realizing that if they shared knowledge across their organization more effectively they could avoid reinventing the wheel, underbid their competitors, and make more profit. The central point is that the first stage of KM was about how to deploy that new technology to accomplish more effective use of information and knowledge.
The first stage might be described as the “If only Texas Instruments knew what Texas Instruments knew” stage, to revisit a much quoted KM mantra. The hallmark phrase of Stage 1 was first “best practices,” later replaced by the more politic “lessons learned.”
Second Stage of KM: HR and Corporate Culture
Within a few years the second stage of KM emerged when it became apparent that simply deploying new technology was not sufficient to effectively enable information and knowledge sharing. It became obvious that human and cultural dimensions needed to be incorporated. The second stage can be described as the “‘If you build it they will come’ is a fallacy” stage. In other words, there was the recognition that “If you build it they will come” is a recipe that can easily lead to quick and embarrassing failure if human factors are not sufficiently taken into account.
It became clear that KM implementation would involve changes in the corporate culture, in many cases rather significant changes. Consider the case above of the new pediatric medicine and the discovery of the efficacy of adding orange juice to the recipe. Pharmaceutical sales reps are compensated primarily not by salary, but by bonuses based on sales results. What is in it for that sales rep to share her new discovery when the most likely result is that next year her bonus would be substantially reduced? The changes needed in corporate culture to facilitate and encourage information and knowledge sharing can be major and profound. KM therefore extends far beyond just structuring information and knowledge and making it more accessible. In particular, the organizational culture needs to be examined in terms of how it rewards information and knowledge sharing. In many cases the examination will reveal that the culture needs to be modified and enriched. Often this will involve examining and modifying how the compensation scheme rewards information and knowledge sharing.
This implies a role for KM that very few information professionals have had to be involved with in the past. The implication is clear that KM leaders should be involved in the decision making process for designing the organization’s compensation policy, a process that is very sensitive politically and fraught with difficulty.
A major component of this second stage was the design of easy-to-use and user-friendly systems. The metaphor that was used was that the interface, the Desktop Interface, should appear almost intuitively obvious, like the dashboard of an automobile. (This was of course before the proliferation of chips in automobiles and the advent of user manuals that were inches thick.) Human factors design became an important component of KM.
As this recognition of the importance of human factors unfolded, two major themes from the business literature were brought into the KM domain. The first of these was Senge’s work on the learning organization (Senge, Peter M., 1990 The Fifth Discipline: The Art and Practice of the Learning Organization.) The second was Nonaka’s work on “tacit” knowledge and how to discover and cultivate it (Nonaka, Ikujiro & Takeuchi, Hirotaka, 1995 The Knowledge-Creating Company: How Japanese Companies Create the Dynamics of Innovation.) Both were not only about the human factors of KM implementation and use; they were also about knowledge creation as well as knowledge sharing and communication. The hallmark phrase of Stage 2 was “communities of practice,” CoPs. A good indicator of the shift from the first to the second stage of KM is that for the 1998 Conference Board conference on KM, there was, for the first time, a noticeable contingent of attendees from HR, human resource departments. By the next year, 1999, HR was the largest single group, displacing IT attendees from first place.
Third Stage of KM: Taxonomy and Content Management
The third stage developed from the awareness of the importance of content, and in particular the awareness of the importance of the retrievability of that content, and therefore the importance of the arrangement, description, and the syndetic structure of that content. Since a good alternative description for the second stage of KM is the “it’s no good if they don’t use it” stage, then in that vein, perhaps the best description for the third stage is the “it’s no good if they try to use it but can’t find it” stage. Another bellwether is that TFPL’s report of their October 2001 CKO (Chief Knowledge Officer) Summit reported that for the first time taxonomies emerged as a topic, and it emerged full blown as a major topic (TFPL, 2001 Knowledge Strategies – Corporate Strategies.) The hallmark phrases emerging for the third stage are content management (or enterprise content management) and taxonomies. At the KMWorld 2000 Conference, a track on Content Management appeared for the first time, and by the 2001 KMWorld Conference, Content Management had become the dominant track. In 2006, KMWorld added a two-day workshop entitled Taxonomy Boot Camp, which not only still continues today, and is a day longer, but has also expanded to international locations. The hallmark terms for the third stage of KM are taxonomy and content.
The third stage continues today and is expanding. A major theme now is “data analytics” and “machine learning” for “enterprise search.” The crux is to be able to effectively manage and retrieve your data without maintaining a stable full of taxonomists. A good recent example derives from Rolls Royce’s sale of a subsidiary company. The buyer was entitled to voluminous files of company records, but how was Rolls Royce to separate those from other records with valuable proprietary data that was not part of the sale, and that Rolls Royce wanted to maintain as proprietary knowledge, amidst a sea of structured and unstructured data? The answer was a major project to taxonomize, organize, index, and retrieve massive amounts of data and records. Data analytics and machine learning were powerful tools to help accomplish this, but notice the word “help.” Those tools will not replace the need for good and intelligent human guidance, training, and oversight.
The author is reminded of an occurrence some years ago at Mitre Corporation, a very information driven organization, before the term KM was even bruited about, when the organization wanted to create an expertise location “file/database.” A senior Vice President’s first thought was that just putting the employee’s resumes online would suffice. A short demonstration convinced him otherwise. One sample search was for employees with expertise in “Defense Logistics,” a topic relevant to an RFP that Mitre was bidding on. The clincher was a resume containing neither word, but with the phase “battlefield re-supply.”
A good idea is to browse the KMWorld website (kmworld.com) for current reports, “white papers,” webinars, etc. on topics such as “text analytics” or “big data” or “cognitive computing.”
Yet one more definition/description
The late 20th Century, extending into the 21st Century, was characterized by an almost continuous stream of information and knowledge-related topics and enthusiasms.
Below is a list of those enthusiasms, in roughly chronological order, with the earlier at the top of the list. In some cases, where it is today not so obvious from the name, there is a brief description of what the topic or the enthusiasm consisted of.
- Minimization of Unallocated Cost—the thesis that for optimal decision making costs should be accurately allocated to products, and as data processing became an ever more important and larger component of an organization’s expenses, it was usually treated as G&A, General and Administrative expenses, and a lower and lower proportion of organizational budgets were clearly allocated to their products, and decision making was suffering.
- I.T. and Productivity
- Data Driven System Design—the thesis that the basis of good system design was not the classic if-then-else flow chart, but was based on the charting of procedures and information flow within the organization, and only then came the if-then-else detailed analysis. This drove a dramatically increased recognition of the importance of data and information in systems design and in an organization’s operations in general.
- Decision Analysis—the addition to the basic systems analysis construct that there is often an unrecognized and unanalyzed option in any decision situation—i.e., to go back and deploy some resources to get better information, and then return and consequently have a better chance of making the optimal decision. Further, one can, in principle, compare the cost of better information with the expected value of a better decision.
- Information Systems Stage Hypotheses--there was a profusion of stage hypotheses in the late 1970s and early 1980s: by Nolan, Rockart, Marchand, Gibson & Jackson, Koenig, and Zachman. All had ramifications for, and were for the most part publicized for, the implementation and management of I.T.
- Managing the Archipelago (of Information Services--the thesis that for primarily historical reasons the information handling responsibilities in an organization are usually administratively scattered like the islands in an archipelago, and that this creates severe administrative and managerial problems, and that only very senior management is in a position to get a handle on the problem, and that it needs to very consciously address the issue.
- I.T. as Competitive Advantage
- Management Information Systems (MIS) to Decision Support Systems (DSS)--the recognition that the disenchantment with MIS was caused primarily by its focus solely on internal information. and that most management decisions depended more on external information, and that DSSs needed to address the issue of access to external information and knowledge.
- Enterprise-Wide Information Analysis—this was IBM’s mantra for promotion to their customers’ senior management that, to be successful, an organization 1) had to define what its enterprise really consisted of, and determine what business it was really in; 2) then it had to analyze and define what decisions it had to make correctly to be successful in that enterprise; 3) then it had to analyze what information it needed to make those decisions correctly, and obtain and process that information.
- Information Resource Management—the concept that information was not only a resource, but was also often a product. The Paperwork Reduction Act mandated that all government agencies appoint a senior administrator in charge of Information Resource Management.
- I.T. and Organizational Structure
- Total Quality Management (TQM) and Benchmarking
- Competitive Intelligence (CI)
- I.T. and the Shift from Hierarchies to Markets--the that better I.T. inevitably shifts the optimal effectiveness trade-off point toward the market end of the central planning to market economy spectrum.
- Business Process Re-Engineering
- Core Competencies
- Data Warehousing and Data Mining (more recently known as Big Data)
- E-Business
- Intellectual Capital
- Knowledge Management
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)—the not very obvious name for the idea of integrating all your business’s I.T. operations under one software suite.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- Enterprise Content Management (ECM)
The list is impressively long, and all these topics and enthusiasms are related to the management of information and knowledge, or the management of information processing functions. It would be very hard to come up with a very much shorter list of management topics and enthusiasms of the same era that were not related to the management of information and knowledge or to the management of information processing functions.
If the list is so long, and they have so major a theme in common, has there not been some recognition that all these trees constitute a forest? Well, there was (Koenig, 2000), and it was called “information driven management,” the name put forward for the “forest” at the time , but it received comparatively little exposure or momentum.
One interesting way to look at KM is that, in fact, KM has expanded to become and is now the recognition of that forest of trees (McInerney and Koenig, 2011), that KM is a much better and more recognized name than “information driven management.” It is interesting that this stream of trees, to mix metaphors, has dwindled dramatically since the appearance of KM as an important topic. It can further be argued that the typical new topic or enthusiasm, the cloud and big data for example, can be seen as emerging from within KM.
Other KM Issues
Tacit Knowledge
The KM community uses the term “tacit knowledge” to mean what is not “explicit knowledge,” and in that usage what is usually meant by “tacit” is implicit knowledge, that which is not explicit or formally captured in some fashion, most obviously the knowledge in people’s heads. A more useful and nuanced categorization is explicit, implicit, and tacit. There is indeed tacit knowledge which only resides in someone’s head. Nonaka uses the story of the tacit knowledge that was necessary to develop a home bread maker. To understand what was needed to design a machine to knead dough properly, it was necessary for the engineers to work with bread makers to get the feel for how the dough needed to be manipulated.
But frankly the extent of knowledge that is truly tacit, like how to get up on water skis, that overlaps with the interests of KM systems is rather small. What is often very extensive is the amount of implicit information that could have been made explicit, but has not been. That it has not been is usually not a failure, but usually simply a cost-effective decision, usually taken unconsciously, that it is not worth the effort. The danger lies in assuming that explicit information is addressed by “collecting” and tacit information by “connecting,” and not examining whether there is potentially important implicit information that could and should be made explicit. The after action comments above under Lessons Learned illustrate this important point.
Knowledge Retention and Retirees
One long standing KM issue is the need to retain the knowledge of retirees. The fact that the baby boomer bulge is now reaching retirement age is making this issue increasingly important. KM techniques are very relevant to this issue. The most obvious technique is the application of the lessons learned idea—just treat the retiree’s career as a long project that is coming to its end and create an after action report, a massive data dump. This idea seems straightforward enough, and debriefing the retiree and those with whom he works closely about what issues they perceive as likely to surface or that could possibly arise is obvious common sense. But only in special cases is the full data dump approach likely to be very useful. When a current employee has a knowledge need, is he or she likely to look for the information, and if so how likely is it that the employee’s search request will map onto the information in the retiree’s data dump?
Much more likely to be useful is to keep the retiree involved, maintaining him or her in the CoPs, involved in the discussions concerning current issues, and findable through expertise locator systems. The real utility is likely to be found not directly in the information that the retiree leaves behind, but in new knowledge created by the interaction of the retiree with current employees. The retiree, in response to a current issue says "it occurs to me that ..." and elicits a response something like “yes, the situation is somewhat similar , but here ...,” a discussion unfolds, the retiree contributes some of the needed expertise, and a solution is generated. The solution arises partially from the retiree’s knowledge, but more from the interaction.
The Scope of KM
Another major development is the expansion of KM beyond the 20th century vision of KM as the organization’s knowledge as described in the Gartner Group definition of KM. Increasingly KM is seen as ideally encompassing the whole bandwidth of information and knowledge likely to be useful to an organization, including knowledge external to the organization—knowledge emanating from vendors, suppliers, customers, etc., and knowledge originating in the scientific and scholarly community, the traditional domain of the library world. Looked at in this light, KM extends into environmental scanning and competitive intelligence.
The additional definition of KM above, “Yet One More Definition of KM,” the forest of the trees, also makes the case that the definition of KM is now very broad.
Is KM here to stay?
The answer certainly appears to be yes. The most compelling analysis is the bibliometric one, simply counting the number of articles in the business literature and comparing that to other business enthusiasms. Most business enthusiasms grow rapidly and reach a peak after about five years, and then decline almost as rapidly as they grew.
Below are the graphs for three hot management topics (or fads) of recent years:
Quality Circles, 1977-1986
Source: Abrahamson ,1996
Source: Abrahamson ,1996
Total Quality Management, 1990-2001Source: Ponzi & Koenig, 2002
Business Process Reengineering, 1990-2001
Source: Ponzi & Koenig, 2002
Source: Ponzi & Koenig, 2002
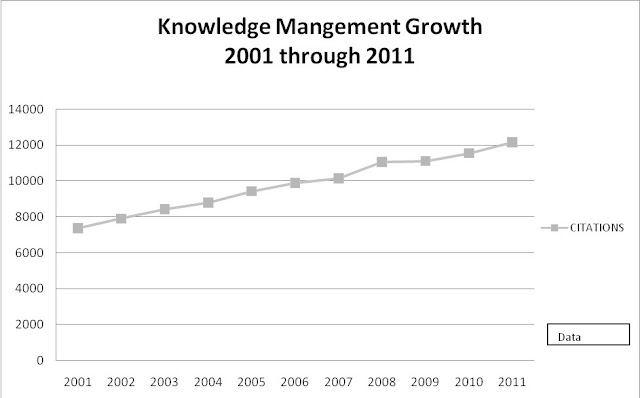
KM looks dramatically different:
| This graph charts the number of articles in the business literature with the phrase “Knowledge Management” in the title. |
If we chart the number of articles in the business literature with the phrase “Knowledge Management” or the abbreviation “KM” in the title, we get the chart below, with an order of magnitude more literature:
It does indeed look as though KM is no mere enthusiasm; KM is here to stay.
References
Abrahamson, E. & Fairchild, G. (1999). Management fashion: lifecycles, triggers, and collective learning processes. Administrative Science Quarterly, 44, 708-740.
Davenport, Thomas H. (1994), Saving IT's Soul: Human Centered Information Management. Harvard Business Review, March-April, 72 (2)pp. 119-131. Duhon, Bryant (1998), It's All in our Heads. Inform, September, 12 (8).
Durham, Mary. (2004). Three Critical Roles for Knowledge Management Workspaces. In M.E.D. Koenig & T. K. Srikantaiah (Eds.), Knowledge Management: Lessons Learned: What Works and What Doesn't. (pp. 23-36). Medford NJ: Information Today, for The American Society for Information Science and Technology.
Koenig, M.E.D. (1990) Information Services and Downstream Productivity. In Martha E. Williams (Ed.), Annual Review of Information Science and Technology: Volume 25, (pp. 55-56). New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishers for the American Society for Information Science.
Koenig, M.E.D. (1992). The Information Environment and the Productivity of Research. In H. Collier (Ed.), Recent Advances in Chemical Information, (pp. 133-143). London: Royal Society of Chemistry. Mazzie, Mark. (2003). Personal Communication.
Koenig, M, E. D. (2000), The Evolution of Knowledge Management, in T. K. Srikantaiah and M. E. D. Koenig, Knowledge Management for the Information Professional. (pp. 23-26), Medford N.J., Information Today, for the American Society for Information Science.
McInerney, Claire, and Koenig, Michael E. D., (2011), Knowledge Management (KM) Processes in Organizations: Theoretical Foundations and Practice, Morgan and Claypool.
Nonaka, I. & Takeuchi, H. (1995). The knowledge creating company: How Japanese Companies Create the Dynamics of Innovation. New York: Oxford University Press.
Ponzi, Leonard., & Koenig, M.E.D. (2002). Knowledge Management: Another Management Fad?" Information Research, 8(1). Retrieved from http://informationr.net/ir/8-1/paper145.html
Ponzi, L., & Koenig, M.E.D. (2002). Knowledge Management: Another Management Fad?", Information Research, 8(1). Retrieved from http://informationr.net/ir/8-1/paper145.html
Prusak, Larry. (1999). Where did Knowledge Management Come From?. Knowledge Directions, 1(1), 90-96. Prusak, Larry. (2004). Personal Communication.
Senge, Peter M.. (1990). The Fifth Discipline: The Art & Practice of the Learning Organization. New York, NY: Doubleday Currency.
Wenger, Etienne C. (1998). Communities of practice: Learning, meaning and identity. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Wenger, Etienne C. & Snyder, W. M. (1999). Communities of practice: The organizational frontier. Harvard Business Review, 78(1), 139-145.
About the Author
Michael E.D. Koenig, Ph.D, is the author or co-author of a number of books on KM, including Knowledge Management in Practice (www.infotoday.com), and numerous articles on the subject of KM. He is Professor Emeritus at Long Island University and is the former and founding dean of the College of Information and Computer Science. In 2015 he received the Award of Merit from the Association for Information Science and Technology, the association’s highest award.